
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Xiamen University, Department of Physics, Xiamen, China
Orbital angular momentum (OAM), emerging as an inherently high-dimensional property of photons, has boosted information capacity in optical communications. However, the potential of OAM in optical computing remains almost unexplored. Here, we present a highly efficient optical computing protocol for complex vector convolution with the superposition of high-dimensional OAM eigenmodes. We used two cascaded spatial light modulators to prepare suitable OAM superpositions to encode two complex vectors. Then, a deep-learning strategy is devised to decode the complex OAM spectrum, thus accomplishing the optical convolution task. In our experiment, we succeed in demonstrating 7-, 9-, and 11-dimensional complex vector convolutions, in which an average proximity better than 95% and a mean relative error <6 % are achieved. Our present scheme can be extended to incorporate other degrees of freedom for a more versatile optical computing in the high-dimensional Hilbert space.
optical computing complex vector convolution orbital angular momentum photonic spatial modes Advanced Photonics Nexus
2023, 2(4): 046008

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Physics and Collaborative Innovation Center for Optoelectronic Semiconductors and Efficient Devices, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
2 School of Physics and Astronomy, SUPA, University of Glasgow, Glasgow G12 8QQ, UK
3 e-mail: chenyy@xmu.edu.cn
4 e-mail: Sonja.Franke-Arnold@glasgow.ac.uk
5 e-mail: chenlx@xmu.edu.cn
While the uncertainty principle for linear position and linear momentum, and more recently for angular position and angular momentum, is well established, its radial equivalent has so far eluded researchers. Here we exploit the logarithmic radial position, , and hyperbolic momentum, , to formulate a rigorous uncertainty principle for the radial degree of freedom of transverse light modes. We show that the product of their uncertainties is bounded by Planck’s constant, , and identify a set of radial intelligent states that satisfy the equality. We illustrate the radial uncertainty principle for a variety of intelligent states, by preparing transverse light modes with suitable radial profiles. We use eigenmode projection to measure the corresponding hyperbolic momenta, confirming the minimum uncertainty bound. Optical systems are most naturally described in terms of cylindrical coordinates, and our radial uncertainty relation provides the missing piece in characterizing optical quantum measurements, providing a new platform for the fundamental tests and applications of quantum optics.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(9): 2223

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Physics and Collaborative Innovation Center for Optoelectronic Semiconductors and Efficient Devices, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
2 Department of Aerospace Science and Technology, Space Engineering University, Beijing 101416, China
3 e-mail: qxd@xmu.edu.cn
4 e-mail: renyuan_823@aliyun.com
5 e-mail: chenlx@xmu.edu.cn
We demonstrated an efficient scheme of measuring the angular velocity of a rotating object with the detection light working at the infrared regime. Our method benefits from the combination of second-harmonic generation (SHG) and rotational Doppler effect, i.e., frequency upconversion detection of rotational Doppler effect. In our experiment, we use one infrared light as the fundamental wave (FW) to probe the rotating objects while preparing the other FW to carry the desired superpositions of orbital angular momentum. Then these two FWs are mixed collinearly in a potassium titanyl phosphate crystal via type II phase matching, which produces the visible second-harmonic light wave. The experimental results show that both the angular velocity and geometric symmetry of rotating objects can be identified from the detected frequency-shift signals at the photon-count level. Our scheme will find potential applications in infrared monitoring.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(1): 01000183
厦门大学物理科学与技术学院物理学系, 福建 厦门 361005
光不仅可以携带自旋角动量,还可以携带轨道角动量。其中,自旋角动量与光波的圆偏振态有关,而轨道角动量来源于光波的螺旋相位结构。自Allen等1992年首次理论确认了光子轨道角动量的物理概念和内涵以来,这类具有特殊螺旋相位波前的新型光场吸引了越来越多的研究兴趣,在经典光学及量子光学领域均展示出了诸多重要的应用前景。本文从基础物理及应用物理两个层面出发,着重介绍了轨道角动量光束的制备与探测技术,特别是近年来轨道角动量调控在螺旋相衬成像技术、远程旋转多普勒效应探测技术及光学微操控技术等领域的研究进展。
量子光学 轨道角动量 螺旋相衬成像 旋转多普勒效应 光学微操控
厦门大学物理科学与技术学院物理学系, 福建 厦门 361005
关联成像以其非定域性、抗干扰能力强等特点得到研究人员的广泛关注,在三维成像、遥感成像、生物医疗、****等领域具有广阔的应用前景。本综述根据发展阶段的不同,详细介绍了纠缠双光子关联成像、(赝)热光关联成像和计算关联成像的发展历程及应用现状,尤其是近年来微光相机(ICCD)的出现为关联成像发展带来的促进作用及最新进展。针对热光关联成像的物理本质进行了简单的讨论,对关联成像的实际应用进行了展望。
成像系统 关联成像 计算成像 成像理论 成像质量 激光与光电子学进展
2020, 57(6): 060001
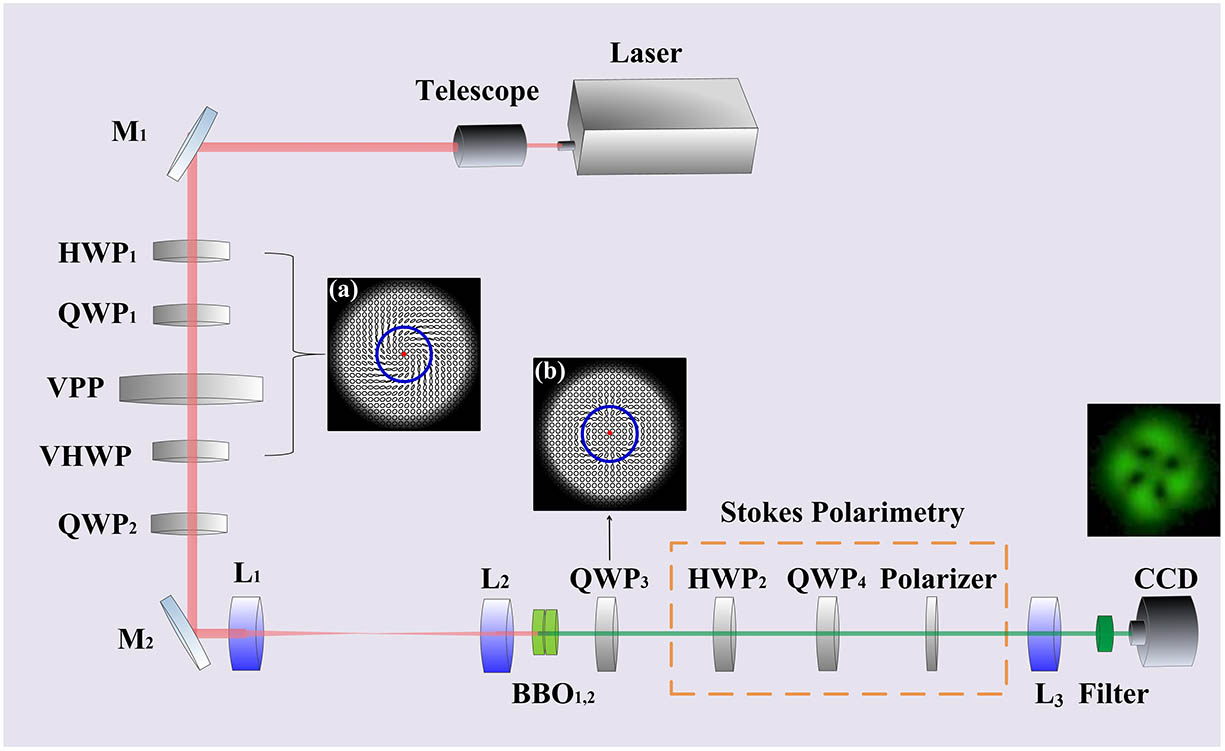
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Foshan University, Foshan 528000, China
2 Department of Physics, Collaborative Innovation Center for Optoelectronic Semiconductors and Efficient Devices, and Jiujiang Research Institute, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
We demonstrate the full vectorial feature of second-harmonic generation (SHG), i.e., from infrared full Poincaré beams to visible full Poincaré beams, based on two cascading type I phase-matching beta barium borate crystals of orthogonal optical axes. We visualize the structured features of the vectorial SHG wave by using Stokes polarimetry and show the interesting doubling effect of the polarization topological index, i.e., a low-order full Poincaré beam is converted to a high-order one. However, the polarization singularities of both C points and L lines are found to keep invariant during the SHG process. Our scheme could offer a deeper understanding on the interaction of vectorial light fields with media and can be generalized to other nonlinear optical effects.
190.2620 Harmonic generation and mixing 260.6042 Singular optics Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(9): 091901
厦门大学物理科学与技术学院, 福建 厦门 361005
从Maxwell方程组出发,将与旋光效应相关的二阶非线性电极化作为线性电极化的微扰项,并结合角谱表示理论,以傍轴高斯光束作为入射光场,研究了光束在具有自然旋光性的Bi12SiO20晶体中的传播问题,并分别采用Minkowski和Abraham两种形式的光动量,得出Bi12SiO20晶体中的光动量及角动量表达式。结果表明,旋光性的存在使得晶体中的Minkowski动量和Abraham动量的比值不再是晶体折射率的平方。采用Minkowski角动量密度形式,可以发现,光场与晶体之间的角动量会发生耦合,虽然光场自身的角动量不守恒,但光场和晶体的总角动量守恒。
物理光学 晶体光学 旋光效应 光动量 角动量 激光与光电子学进展
2019, 56(13): 132601
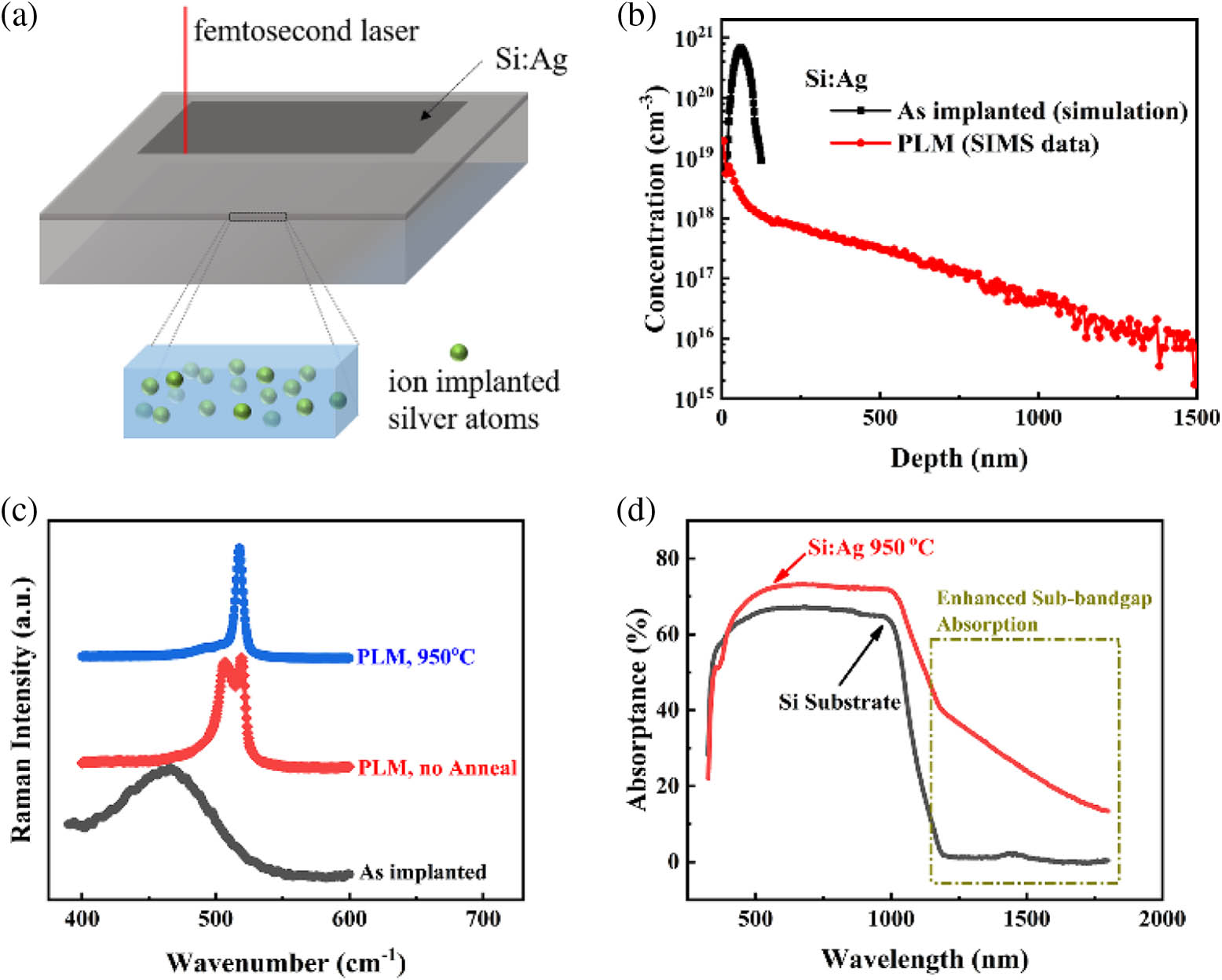
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Silicon Materials and School of Materials Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
2 e-mail: yuxuegong@zju.edu.cn
3 e-mail: mseyang@zju.edu.cn
Developing a low-cost, room-temperature operated and complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) compatible visible-blind short-wavelength infrared (SWIR) silicon photodetector is of interest for security, telecommunications, and environmental sensing. Here, we present a silver-supersaturated silicon (Si:Ag)-based photodetector that exhibits a visible-blind and highly enhanced sub-bandgap photoresponse. The visible-blind response is caused by the strong surface-recombination-induced quenching of charge collection for short-wavelength excitation, and the enhanced sub-bandgap response is attributed to the deep-level electron-traps-induced band-bending and two-stage carrier excitation. The responsivity of the Si:Ag photodetector reaches 504 mA· W 1 at 1310 nm and 65 mA ·W 1 at 1550 nm under 3 V bias, which stands on the stage as the highest level in the hyperdoped silicon devices previously reported. The high performance and mechanism understanding clearly demonstrate that the hyperdoped silicon shows great potential for use in optical interconnect and power-monitoring applications.
Photonics Research
2019, 7(3): 03000351

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Physics, Jiujiang Research Institute and Collaborative Innovation Center for Optoelectronic Semiconductors and Efficient Devices, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361005, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, School of Physics and Astronomy, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
3 e-mail: xfchen@sjtu.edu.cn
4 e-mail: chenlx@xmu.edu.cn
The generation and manipulation of optical vortices are of fundamental importance in a variety of promising applications. Here, we develop a nonlinear optical paradigm to implement self- and cross-convolution of optical vortex arrays, demonstrating the features of a vortex copier and regenerator. We use a phase-only spatial light modulator to prepare the 1064 nm invisible fundamental light to carry special optical vortex arrays and use a potassium titanyl phosphate crystal to perform type II second-harmonic generation in the Fourier domain to achieve 532 nm visible structured vortices. Based on pure cross-convolution, we succeed in copying arbitrary-order single vortices as well as their superposition states onto a prearranged array of fundamental Gaussian spots. Also, based on the simultaneous effect of self- and cross-convolutions, we can expand the initial vortex lattices to regenerate more vortices carrying various higher topological charges. Our presented method of realizing an optical vortex copier and regenerator could find direct applications in optical manipulation, optical imaging, optical communication, and quantum information processing with structured vortex arrays.
Optical vortices Harmonic generation and mixing Nonlinear optical signal processing Photonics Research
2018, 6(6): 06000641
厦门大学物理科学与技术学院, 福建 厦门 361005
利用非线性频率转换过程获得高阶涡旋光场的方法得到了研究人员的广泛关注, 目前关于该领域的研究大都集中在拉盖尔-高斯光束方面, 而针对复合涡旋的非线性频率转换过程的研究不多。从理论方面分析了复合涡旋的倍频过程, 得出了其倍频光场的涡旋分布, 证明了复合涡旋倍频过程中拓扑荷数守恒。在实验方面, 基于非线性光学晶体磷酸钛氧钾, 验证了拉盖尔-高斯涡旋光倍频过程中的拓扑荷数守恒。基于马赫-曾德尔干涉仪产生复合涡旋光, 并研究了其倍频过程。实验结果表明, 复合涡旋光在倍频过程中的拓扑荷数仍然守恒。
非线性光学 倍频 守恒 复合涡旋 拓扑荷数 激光与光电子学进展
2017, 54(5): 051901





